A Technical History Through the Tools, Upgrades, and Real-World Administration That Shaped Modern Email
Email administration today looks nothing like it did in the mid-1990s. What began as a system of flat files and small IS databases has evolved into a globally distributed, cloud-secure service powered by modern authentication, forensic automation, and layered identity protections.
This article covers the full evolution — from Exchange 5.0 → 5.5 → 2000 → 2003 → 2007 → 2010 → 2013 → 2016 → Hybrid → Exchange Online — through the practical tools and real operational practices that defined each era.
It also highlights legacy repair tools (ISINTEG, ESEUTIL), the emergence of PowerShell, and modern security controls such as DKIM, DMARC, and real-time EXO policies.
1. Exchange 5.0 — The GroupWise Era & The Limits of Early Messaging
When Exchange 5.0 existed, Novell GroupWise was still considered the enterprise email standard. Capacity was limited and reliability required constant hands-on administration.
Key Characteristics
- Basic directory service
- Small private and public folder stores
- No Active Directory yet
- No PowerShell
- 16GB database ceiling
- Frequent corruptions under heavy load
Real Tools Used
🔧 ISINTEG — Logical Database Repair
Example usage:
ISINTEG -pri -fix -test alltests
🔧 ESEUTIL — Physical Database Repair
Soft recovery:
ESEUTIL /r E00 /l "E:\logs" /d "E:\mdbdata"
Hard recovery:
ESEUTIL /p "E:\mdbdata\priv.edb"
Defrag/whitespace removal:
ESEUTIL /d "E:\mdbdata\priv.edb"
White space mattered because the database could never exceed the size limit, and defrags were essential to survive weekly growth.
2. Exchange 5.5 — The First True Enterprise Version
Exchange 5.5 replaced GroupWise in many organizations because it solved the two biggest weaknesses:
Major Improvements
- Larger database limits
- Internet Mail Connector (IMC) matured
- Directory replication across sites
- Better MAPI stability
- More predictable backups
This was the version where large organizations first began to trust Exchange for hundreds or thousands of users.
Database limitations still required:
- Regular whitespace removal
- Offline defrags
- ISINTEG repairs
3. Exchange 2000 / 2003 — Active Directory Arrives
The introduction of Active Directory changed everything.
Now Possible
- Kerberos authentication
- Unified Global Address List
- Recipient policies
- Improved SMTP stack
- Better routing groups
Tools of the Era
- ESEUTIL still required
- ISINTEG for logical repair
- Streaming file (.STM) management
- COM+ based transport pipeline
Disaster recovery still required:
- Hard repairs
- Log replays
- Offline maintenance windows
4. Exchange 2007 — PowerShell Revolutionizes Email Administration
Exchange 2007 was the turning point. This version introduced:
Major Innovations
- PowerShell (EMS)
- Role-based server architecture
- Database Availability Groups (DAGs begin later)
- Transport rules
- Modern SMTP pipeline
Example PowerShell Operations
Bulk mailbox creation
Import-Csv users.csv | % {
New-Mailbox -UserPrincipalName $_.UPN -Name $_.Name -Alias $_.Alias
}
Transport rule creation
New-TransportRule -Name "Block EXE" -AttachmentExtensionMatchesWords ".exe" -RejectMessageReason "Executable blocked"
Database health
Get-MailboxDatabaseCopyStatus *
PowerShell replaced ISINTEG as the primary troubleshooting interface.
5. Exchange 2010 / 2013 — High Availability & Hybrid Era
These versions supported:
- DAGs with multiple copies
- Outlook Anywhere (RPC over HTTPS)
- Cross-forest migrations
- Massive mailboxes (50GB+)
- First large-scale hybrid deployments
Database Whitespace Management
Modern approach:
Get-MailboxDatabase -Status | ft Name,AvailableNewMailboxSpace
To reclaim all space:
- Create new database
- Move mailboxes
- Remove old database
- Mount clean database
Multi-region examples
- Databases per region (NA/APAC/EMEA)
- Public folder migrations
- CAS/Hub/MBX role separation
6. On-Prem to Cloud Migrations — AWS WorkMail, Exchange 2010, Hybrid, EXO
Organizations with large global footprints began migrating:
Migration Examples
- From AWS WorkMail → Exchange 2013 HA → EXO
- From Exchange 2010 datacenters → Hybrid → EXO
- From Exchange 2013 → EXO using HCW and staged cutover
Challenges Solved by EXO
- No more ESEUTIL
- No more ISINTEG
- No more DAG patching
- No more weekend downtimes
- Automatic redundancy
- Modern authentication
- Better malware scanning
7. Exchange Online — The Modern Cloud Era
Today, administrators rely on:
- Exchange Online PowerShell v3
- Graph API
- Defender for O365
- Purview eDiscovery
- Modern connectors
- DKIM / DMARC enforcement
- Real-time spam intelligence
- Modern auth for SMTP
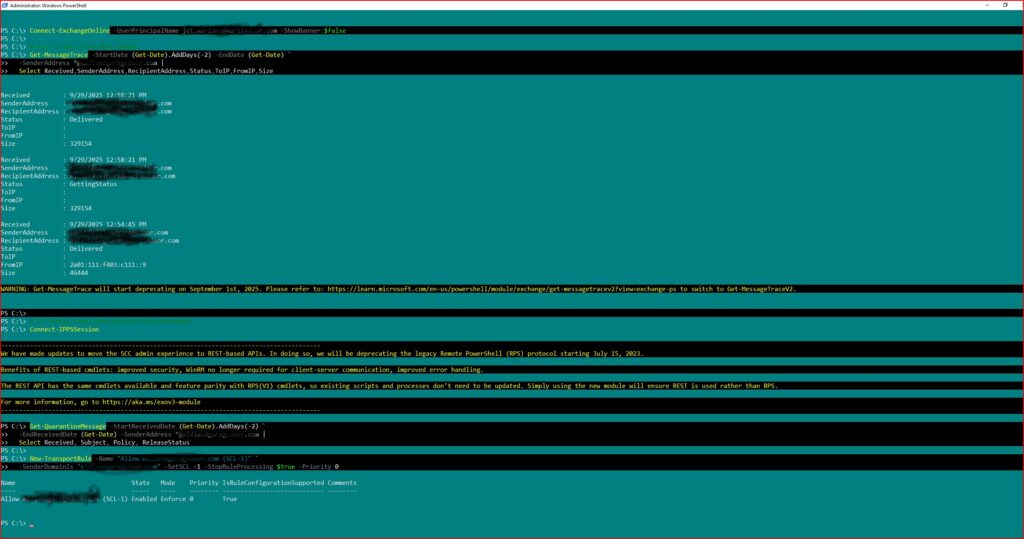
How to Rotate DKIM 2048-bit Keys
Admin Center → Security → Email Authentication → DKIM → Rotate Keys
Verify in PowerShell
Get-DkimSigningConfig | fl Domain,Selector1CNAME,Selector2CNAME
Keys should be:
- 2048-bit
- Rotated regularly
- Protected from unauthorized access
**8. Real-World Security Hardening in EXO
(Including the Kill-Switch Scripts)**
Last-generation threats require immediate defensive controls.
These are sanitized versions of the two emergency scripts used to block impersonation attacks:
🛑 Kill Switch Transport Rule (Blocks All External Sender Impersonation)
New-TransportRule -Name "KILL-SWITCH" `
-FromScope NotInOrganization `
-SentToScope InOrganization `
-SetHeaderName "X-Blocked" `
-SetHeaderValue "EmergencyBlock" `
-StopRuleProcessing $true `
-Enabled $true `
-Mode Enforce
🛑 Block-All Impersonation Rule
New-TransportRule -Name "BLOCK-IMPERSONATION" `
-HeaderMatchesMessageHeader "From" `
-HeaderMatchesPatterns ".*@yourdomain\.com" `
-SentToScope InOrganization `
-FromScope NotInOrganization `
-RejectMessageReasonText "External sender attempted domain impersonation" `
-StopRuleProcessing $true
After the event is over, disable:
Disable-TransportRule "KILL-SWITCH"
Disable-TransportRule "BLOCK-IMPERSONATION"
9. Why Exchange Online Beats Every On-Prem Version
No More:
- Database corruption
- ESEUTIL repair weekends
- ISINTEG logical rebuilds
- Streaming file failures
- Whitespace management
- RPC failures
- CAS array dependency
Instead You Get:
- Multi-region HA
- Continuous patching
- DKIM / DMARC alignment
- Modern authentication
- Real-time message trace
- Defender Safe Links/Safe Attachments
- Purview forensic tools
- 24/7 cloud threat intelligence
10. Summary
This blog ties together:
- The original on-prem tools (ISINTEG, ESEUTIL)
- The arrival of AD
- The PowerShell revolution
- The hybrid era
- The modern cloud security stack
- DKIM rotation
- EXO forensic investigation
- Emergency transport rule defense
It shows why the move from Exchange 5.0 to EXO was inevitable — every stage improved reliability, scalability, administration, and security.
© 2012–2025 Jet Mariano. All rights reserved.
For usage terms, please see the Legal Disclaimer.